This article was originally published in Infinite Energy Magazine here.
CHASE PETERSON, FORMER PRESIDENT OF UNIVERSITY OF UTAH, DIES
by Marianne Macy
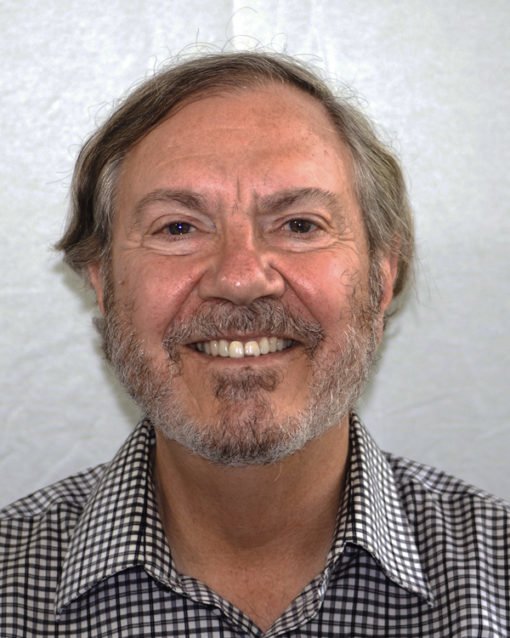
Chase Nebeker Peterson, former President of University of Utah, died on September 14, 2014 from complications of pneumonia. His life story was traced in his 2012 autobiography, The Guardian Poplar: A Memoir of Deep Roots, Journey, and Rediscovery. The concept of roots were important to Chase Peterson. He never forgot his own from a family of Mormon pioneers, despite a life that would take him from his birthplace of Logan, Utah to elite eastern prep schools and Harvard University, from which he was an undergraduate and graduate of the medical school. In 2006, Peterson received the Harvard Medal, awarded at commencement by the Alumni Association for a “lifetime contribution to Harvard.” He had three official careers—Vice President of Harvard University, Vice President for Health Services at the University of Utah, and President of the University of Utah. He also practiced medicine and taught his last class in July of 2014. He was a public spokesperson for innovation at the institutions he was associated with, an innovator, administrator who instituted an open door policy with students, doctor, writer, and visionary.
Cornel West, philosopher, best-selling author, civil rights activist, saluted Chase Peterson for “his prophetic witness at Harvard in the turbulent 60s and 70s, his promotion of black priesthood in the Mormon church, his support of anti-apartheid protest in the 1980s, and his steadfast defense of academic freedom during the cold fusion controversy in the early 90s—all expressed his quiet and humble effort to be true to himself.”
MSNBC’s Lawrence O’Donnell, Jr. heard that Dr. Chase Peterson had died and put a moving tribute on air that saluted Peterson for his historically important actions at Harvard which included hiring the first African-American admissions staff member, instituting an enrollment strategy to embrace students less privileged than the typical Ivy League undergraduate—which, as it turned out, included O’Donnell himself, whose admissions entry interview was with Chase Peterson. The United States Supreme Court cited the measures Chase Peterson instituted as exemplary.
In 1978 Peterson had returned from Harvard to the University of Utah as Vice President in charge of health sciences and the university hospital program. There he found “a unique culture.” The University of Utah, he wrote, offered “an unfettered opportunity to restless young faculty members” who would not face the restraints imposed by more settled places. “Ambitious people—often mavericks held back by practices at other institutions—found comfort and support at the University of Utah.” In his book, Peterson mentioned Max Wintrobe, who in the 1940s was the leading hemotologist, texbook author and junior professor at John Hopkins, where he felt at the time he hit a glass ceiling of anti-Semitism at the otherwise excellent institution. Wintrobe, Peterson wrote, felt Utah, while lacking the research budgets of the institutions in the east, “nevertheless presented unlimited opportunity—a new Zion as it were—open to a Jew or anyone else smart and hard-working enough to take advantage of possibilities. As chief of the Department of Internal Medicine, he brought with him a critical mass of respected young medical investigators. Even more importantly, he brought a personal level of excellence that was infectious and launched Utah toward the upper ranks of medical schools and centers.” Peterson also pointed out that this receptive climate was historically illustrated in 1916, when Utah elected the second Jewish governor in the United States, Simon Bamberger, who was widely admired. He added that Bamberger had called the Utah Legislature into special session to ratify the national woman’s suffrage amendment.
Salt Lake City’s University of Utah is the “economic engine for the state,” a phrase coined by former University President David Gardner. Chase Peterson throughout his career valued his home state for its pioneering spirit and what to him was the epitome of American opportunity. Peterson worked to establish a nationally recognized center of medical research, with special contributions in genetic research and the high profile recognition for being the site of the first human heart implant based on research done by Dr. Willem Kolff. In 1982 Kolff’s results were approved by the FDA. In December 1982 the chief surgeon, Dr. William DeVries, operated on Barney Clark and implanted the artificial heart. Chase Peterson was the face of the University, giving twice a day reports to the assembled international media. In his memoir, Dr. Chase Peterson discussed the extraordinary events, but in a narrative twist completely his own finished his in-depth account of the medical breakthrough with the sort of question that Peterson attributed to the extraordinary world fascination with the story. Chase Peterson wrote that Barney Clark’s wife had told Chase right before surgery Barney had asked, “I wonder if I will still love you when I lose my heart?” Peterson wrote, “He answered that question a few days post-op when—still reduced whispering around a tracheotomy tube—he gestured to his wife and mouthed the words, ‘I love you.’ The scalpel had met its match. Love required a functional pump, but its home was elsewhere.”
Chase Peterson’s tenure and tributes are marked with mentions of his leadership, enthusiasm and generosity. Others remarked on his courage and support of academic freedom, freedom of inquiry and pursuit of ideas. To Peterson, this was a sacred trust he felt was his mission to uphold. His obituaries mentioned controversies of his tenure as University President, what he wrote of as the “perfect storm” on conflicting interests and opinions over Martin Fleischmann and Stanley Pons’ discovery and work on cold fusion at the University of Utah. The variety of descriptions reflected on the field now in Peterson’s obituary accounts illustrate the spectrum of those perspectives. Chase Peterson never stopped believing it was his job and responsibility to support the freedom of research, no matter the personal cost to himself and his family, no matter the warnings of no less an advisor than Nobel laureate Hans Bethe, who told him ahead of time, “They will only laugh at you.”
Peterson wrote in his memoir: “No president, dean or department chair at any research university can arbitrarily influence the publication or suppression of something against a faculty member’s will, whether that something is a chemical process, a better can opener, a concerto, a play, a piece of writing, or anything else. Neither can a faculty member’s right to publish or circulate something be prevented. Such action violates academic freedom in its most basic sense.”
If cold fusion could work, Chase Peterson said, it would be as important as the discovery of fire. The local NPR station in Salt Lake City rebroadcast a program on Peterson’s book this week that quoted him as saying this. More important was the right to pursue cold fusion, or any idea. Chase Peterson’s support of cold fusion was instrumental in costing him the presidency of the University of Utah. He often stated that he would do it all over again. Patrick Shea, who had served as counsel to Fleischmann and Pons, this week reflecting on Chase Peterson’s death commented, “No University of Utah president has ever done as much to support his faculty and their academic freedom.”
Chase Peterson is survived by his wife Grethe Ballif Peterson, his children Stuart and Edward Peterson, Erika Munson, and thirteen grandchildren. His memorial service will be held on September 27th at 10:00 am in the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints Monument Park North Stake.
Marianne Macy has been doing oral histories relating to the history of cold fusion since 2007 and is writing a book on cold fusion’s start to the present day. An excerpt from the book will run in Issue 118 of Infinite Energy.
Related Links
The Guardian Poplar: A Memoir of Deep Roots, Journey, and Rediscover by Chase Nebeker Peterson
Cold Fusion Now Cross-Country Tour Ruby Carat visits the University of Utah campus.